Calculate PRFs for single station¶
Prepare seismic records order by stations¶
Seismic data including direct P arrival should be trimmed according earthquakes. Meanwhile, the data should be order by stations instead of events. For example, YN001 and YN002 are stations; the SAC files are teleseismic data records of these stations.
event_data/
├── YN001
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.1.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.2.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.3.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.22.06.55.1.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.22.06.55.2.sac
│ │......
├── YN002
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.1.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.2.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.15.35.02.3.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.22.06.55.1.sac
│ ├── 2018.229.22.06.55.2.sac
│ │......
Calculate PRFs using a simple command¶
Prepare a configure file¶
We should prepare a configure file as following including all parameters that will be set during the calculation. The format is following Python module of configparser. We have provided a template configure file in RF calculation. See comment in detail.
Run in command line¶
We have provided the command prf. The usage is shown as:
usage: prf [-h] [-l] [-r N|E|NE] [-s] [-b [BAZ]] [-w] [-f finallist] cfg_file
Calculating RFs for single station
positional arguments:
cfg_file Path to RF configure file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l use local catalog, defaults to false
-r N|E|NE Reverse components: N, E or NE
-s Switch the East and North components
-b [BAZ] Correct back-azimuth. If "baz" is specified, the corr_baz = raw_baz + baz. If there is no argument, the back-azimuth will be corrected with minimal energy
of T component. The searching range is raw_baz +/- 90
-w Write project to localfile
-f finallist Specify finallist for re-calculating RFs and -l is invalid in this pattern
cfg_file: configure file.-lif the argument was specified, a local file of catalog would be used in searching earthquakes.-rReverse the horizontal components. The arguments should be inEN,EorN.-sIf this option is specified, the East and North components would be changed.-bCorrect back-azimuth. If \(baz\) is specified, the \(baz_{corr} = baz_{raw} + baz\). If no arguments following-b, back-azimuth will be corrected for grid searching minimal energy of T component. The searching range is \(baz_{raw} \pm 90^{\circ}\)-fAdd a path to final-list following this option. Event information in the final-list is used instead of searching earthquakes from catalog.
Initialize a project instance¶
To further understand the procedure of the command prf , we recommend calculating PRFs with writing a Python script as following steps.
First, let’s initialize a RFinstance. In this instance, we can set parameters and calculate PRFs using functions of the class.
from seispy.rf import RF
from os.path import join
from obspy import UTCDateTime
pjt = RF()
Set parameters¶
Most of parameters are saved in the class pjt.para. All default parameters are shown as following
print(pjt.para.__dict__)
{'_datapath': '/Users/xumj',
'_rfpath': '/Users/xumj',
'_imagepath': '/Users/xumj',
'_catalogpath': '/Users/xumj/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.3.1/lib/python3.7/site-packages/seispy-1.1.8-py3.7.egg/seispy/data/EventCMT.dat',
'offset': None,
'tolerance': 210,
'dateformat': '%Y.%j.%H.%M.%S',
'date_begin': 1976-01-01T00:00:00.000000Z,
'date_end': 2019-07-11T14:04:15.365860Z,
'magmin': 5.5,
'magmax': 10,
'dismin': 30,
'dismax': 90,
'ref_comp': 'BHZ',
'suffix': 'SAC',
'noisegate': 5,
'gauss': 2,
'target_dt': 0.01,
'phase': 'P',
'time_before': 10,
'time_after': 120,
'only_r': False}
Thus, we can set them in our scripts
pjt.para.datapath = 'Data/Path/to/station_name'
pjt.para.rfpath = 'Result/Path/to/station_name'
pjt.para.suffix = 'sac'
pjt.para.ref_comp = ".1."
pjt.date_begin = UTCDateTime('20180701')
pjt.date_end = UTCDateTime('20190701')
pjt.para.offset = 0
pjt.para.tolerance = 60
or in a configure file as above. When you want to initialize an instance using this configure file, please add the path to RF() as:
pjt = RF(cfg_file='path/to/config')
Search earthquakes from catalog¶
We use the same procedure as the SplitRFLab. To match the data records and events, we should search earthquakes with some criteria (period, epicentral distance and magnitude).
Load station information¶
the The station latitude and longitude are absolutely necessary when we are used to search earthquakes. the function will read stla and stlo of SAC header from files in pjt.para.datapath.
pjt.load_stainfo()
Search earthquakes¶
the function provide two method to search earthquakes. use
pjt.search_eq()
to search earthquakes in IRIS Web service with the CMT catalog.
In addition, the function allow to prepare earthquakes from a CMT catalog file (defaults to seispy/seispy/data/EventCMT.dat). Use command updatecatalog to update this default catalog file.
pjt.search_eq(local=True)
Associate SAC files with events¶
This is a important step, which allow to link SAC files with teleseismic events in catalog. The pjt.para.dateformat, that is a format string as in time.strftime, including datetime information as a reference time for event association. For example, assuming the filename is 2018.229.15.35.02.1.sac. the pjt.para.dateformat should be %Y.%j.%H.%M.%S.
A reference sac file will read to Associate with events. Thus, file-search-string will help to find real SAC files in data path. The file-search-string composed of pjt.para.ref_comp and pjt.para.suffix. The presence of *pjt.para.ref_comp*pjt.para.suffix, such as *.1.*sac in this example.
The pjt.para.offset and pjt.para.tolerance are used to match the origin time from catalog. The origin time in the catalog \(t_o\) should be in the range of
Note
The
offsetis the time duration between the event time and the starting time of your seismograms. Ideally, this offset should be identical to the “request start time” defined in the previous window but the data management center may have sent you data beginning later than requested. The offset value represents this difference.The
Tolerancevalue in seconds will define the time window within which the program will try to associate a seismic file to an event file, by using either its name or the information contained in the header. It is up to the user to find the best compromise: a value too small will let orphans and a value too large will bring confusion since several files could be associated to a seismic event.
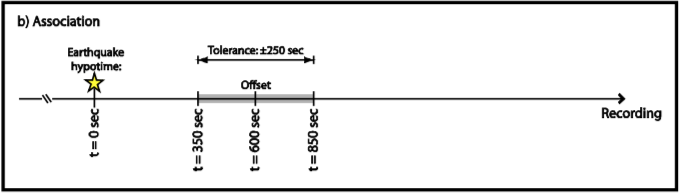
After setting up these parameters, use following command to associate data records to the catalog:¶
pjt.match_eq()
Pre-processing¶
The process of pretreatment include detrend, bandpass filter, calculating arrival time, reject bad record with low SNR, trim records and rotate components from NE to RT.
Filter¶
We will apply a bandpass filter on seismic records. Two corners should be specified.
para.freqmin: Pass band low corner frequency.para.freqmax: Pass band high corner frequency.
Signal-noise-ratios (SNR) calculation¶
seismic records with poor quality will be rejected in this step. We will reject records with SNR < para.noisegate. The SNR was calculated as:
where \(A_N\) and \(A_N\) are root mean squares (RMS) of the waveform trimmed with time length of para.noiselen before and after theoretical P arrival times, respectively.
Trim¶
The waveforms will be cut in this step before para.time_before and after para.time_after theoretical P arrival times, respectively.
pjt.detrend()
pjt.filter() # default using 'para.freqmin' and 'para.freqmax'
pjt.cal_phase()
pjt.drop_eq_snr() # The threshold used as 'para.noisegate'
pjt.trim() # from 'para.time_before' before P to 'para.time_after' after P
pjt.rotate()
Saving and loading this project¶
Save this project¶
The class RF provided method to save the parameters and associated seismic events.
pjt.save('path/to/pjt.pkl')
A pkl file will be saved into local path, which include the subclass pjt.para and pjt.eqs. The pjt.eqs is a DataFrame instance with following columns
Column |
Implication |
|---|---|
|
Origin time of the event |
|
Latitude of the event |
|
Longitude of the event |
|
Focal depth of the event |
|
Magnitude of the event |
|
Back-azimuth between the station and the event |
|
Great arc distance between the station and the event |
|
Datetime field in the associated SAC filename |
Load this project¶
Create a new project and load the save project file for RF recalculation.
newpjt = RF()
newpjt.load('path/to/pjt.pkl')
Note
The waveform data will not be saved into file. So please ensure that the data files are exists in the
newpjt.para.datapath.The data files will be reload via
newpjt.load('path/to/pjt.pkl'). Thus the pretreatment is necessary in recalculation.
PRFs calculation¶
We need parameters of pjt.para.gauss, pjt.para.itmax and pjt.para.minderr to calculate PRFs using iterative time-domain deconvolution method
pjt.para.gauss: Gauss factor. Default is 2.0.pjt.para.itmax: The maximum number of iterations. Default is 400.pjt.para.minderr: The minimum misfit. Default is 0.001.
pjt.deconv()
Save PRFs¶
Save the PRFs to pjt.para.rfpath with some criteria. Two kind of criteria allow to set (i.e., crust or mtz). if the parameter set as None, all of PRFs will be saved.
crustThe maximum peak should appear between -2s and 2s.
mtzThe maximum peak should appear between -5s and 5s.
the maximum amplitudes of PRFs in a 30–120 s window after the direct P are smaller than 30% of the maximum amplitudes of the direct P phases.
pjt.saverf(criterion='crust')