Calculate a P-wave Receiver Function (PRF)¶
Note
This notebook can be downloaded as
PRF_Process.ipynbTeleseismic waveforms can be downloaded as
rf_example.tar.gz
1. Import corresponding modules¶
import obspy
import seispy
from seispy.decon import RFTrace
%matplotlib inline
2. Read SAC files with 3 components (ENZ)¶
You should perpare teleseismic data if SAC format (ENZ) and read them via obspy. To facilitate the follow-up, you’d better write positions of the station and the event into SAC header (i.e., stla, stlo, evla, evlo and evdp).
st = obspy.read('../_static/files/rf_example/*.101.*.SAC')
3. Pre-process for raw data¶
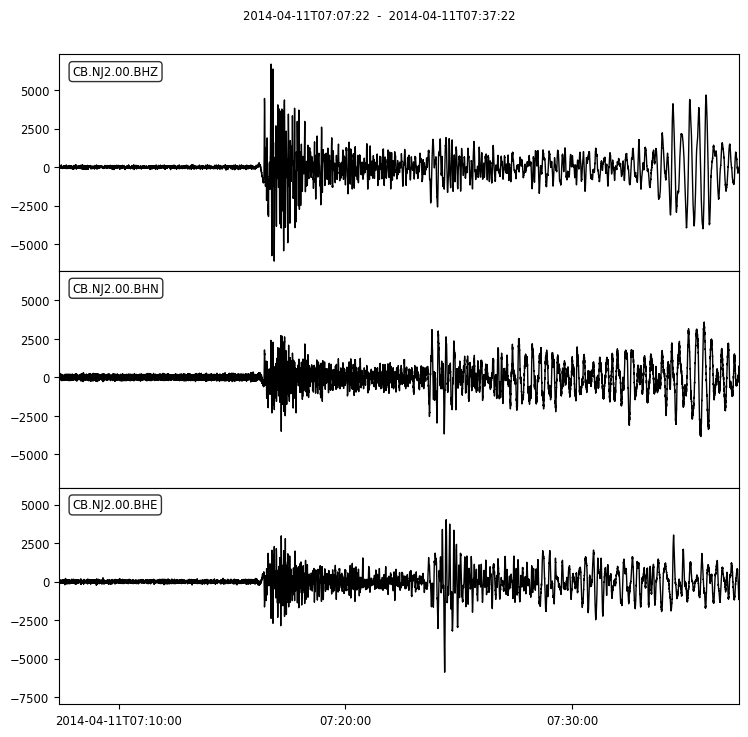
You should remove the mean offset and linear trend of the waveforms, then filtered them with a Butterworth bandpass filter in the range of 0.05–2 Hz. The figures show a comparison between the raw data and the data after pre-process
st.detrend()
st.filter("bandpass", freqmin=0.05, freqmax=2.0, zerophase=True)
st.plot()

4. Calculate the epicenter distance and back-azimuth¶
To trim the waveform or rotate the components, you can use the seispy.distaz to calculate the epicenter distance and back-azimuth.
da = seispy.distaz(st[0].stats.sac.stla, st[0].stats.sac.stlo, st[0].stats.sac.evla, st[0].stats.sac.evlo)
dis = da.delta
bazi = da.baz
ev_dep = st[0].stats.sac.evdp
print('Distance = %5.2f˚' % dis)
print('back-azimuth = %5.2f˚' % bazi)
Distance = 51.64˚
back-azimuth = 131.59˚
5. Rotation¶
Now you can rotate horizontal components (ENZ) into radial and transverse components (TRZ)
st_TRZ = st.copy().rotate('NE->RT', back_azimuth=bazi)
6. Estimating P arrival time and ray parameter by obspy.taup¶
from obspy.taup import TauPyModel
model = TauPyModel(model='iasp91')
arrivals = model.get_travel_times(ev_dep, dis, phase_list=['P'])
P_arr = arrivals[0]
7.Trim the waveforms for PRF¶
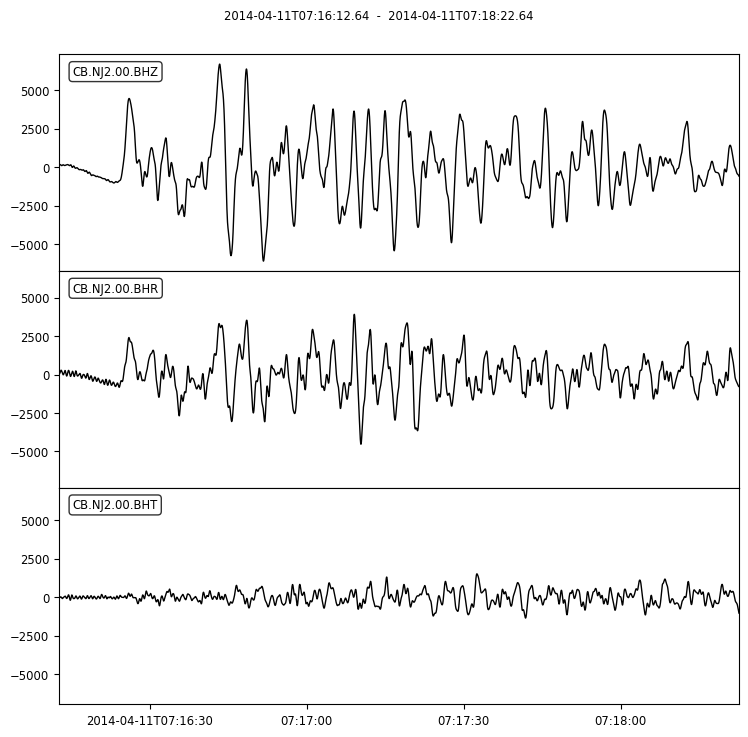
Then you cut 130 s long waveforms around P arrival time (from 10 s before to 120 s after theoretical P arrival times).
dt = st[0].stats.delta
shift = 10
time_after = 120
st_TRZ.trim(st_TRZ[0].stats.starttime+P_arr.time-shift,
st_TRZ[0].stats.starttime+P_arr.time+time_after)
time_axis = st_TRZ[0].times() - shift
st_TRZ.plot(show=False)

8. Calculate PRF¶
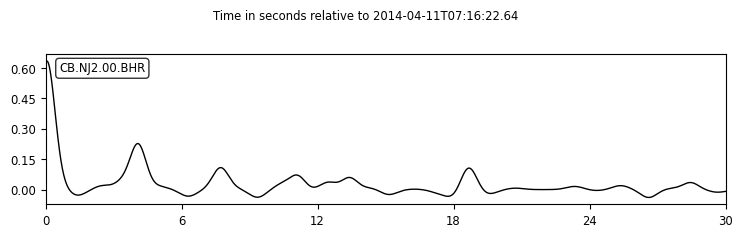
seispy.decon.RFTrace provide a class for deconvolution. Now let’s Calculate a PRF with iteration time-domain deconvolution mehtod. In this example, we assume:
Gauss factor = 2.0
The maximum number of iterations = 400
Minimum error = 0.001
f0 = 2.0
itmax = 400
minderr = 0.001
rf = RFTrace.deconvolve(st_TRZ[1], st_TRZ[2], method='iter',
tshift=shift, f0=f0, itmax=itmax, minderr=minderr)
rf.plot(show=False, type='relative',
starttime=rf.stats.starttime+shift,
endtime=rf.stats.starttime+shift+30)

9. Write PRF to SAC file¶
Finally, you can write the PRF to a SAC file with seispy.deconv.RFTrace.write function. The PRF will be saved in the SAC file.
from seispy.geo import srad2skm
rf.write('PRF.sac', user1=srad2skm(P_arr.ray_param))